Optics Ques 167
- The Young’s double slit experiment is done in a medium of refractive index $4/3$. A light of $600 $ $nm$ wavelength is falling on the slits having $0.45$ $ mm$ separation. The lower slit $S _2$ is covered by a thin glass sheet of thickness $10.4$ $ \mu m$ and refractive index $1.5$. The interference pattern is observed on a screen placed $1.5$ $m$ from the slits as shown in the figure.
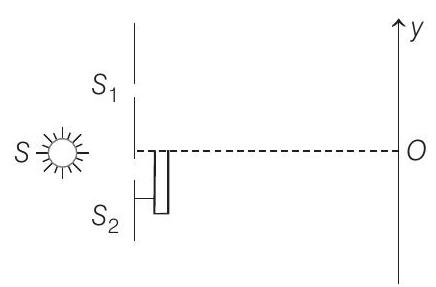
(a) Find the location of central maximum (bright fringe with zero path difference) on the $y$-axis.
(b) Find the light intensity of point $O$ relative to the maximum fringe intensity.
(c) Now, if $600 $ $nm$ light is replaced by white light of range $400$ to $700 $ $nm$, find the wavelengths of the light that form maxima exactly at point $O$.
(All wavelengths in the problem are for the given medium of refractive index $4 / 3$. Ignore dispersion)
$(1999,10 M)$
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 167.(a) $4.33 $ $mm \quad $ (b) $I=\frac{3 I _{\max }}{4} \quad $ (c) $650$ $ nm ; 433.33 $ $nm$
Solution:
Formula:
- Given, $\lambda=600 $ $ nm=6 \times 10^{-7}$ $ m$,
$ \begin{aligned} d & =0.45 mm=0.45 \times 10^{-3} m, \\ D & =1.5 m . \end{aligned} $
Thickness of glass sheet, $t=10.4 $ $\mu m=10.4 \times 10^{-6}$ $ m$
Refractive index of medium, $\mu _m=4 / 3$
and refractive index of glass sheet, $\mu _g=1.5$
(a) Let central maximum is obtained at a distance $y$ below point $O$. Then $\Delta x _1=S _1 P-S _2 P=\frac{y d}{D}$
Path difference due to glass sheet
$ \Delta x _2=(\frac{\mu _g}{\mu _m}-1 )t $
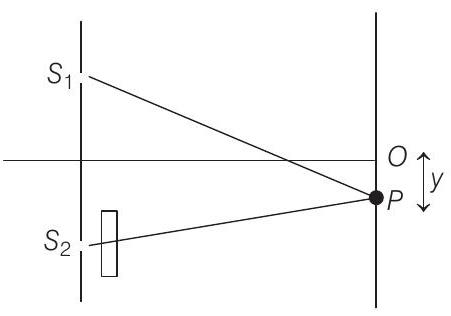
Net path difference will be zero when
$ \Delta x _1 =\Delta x _2 $
$\text { or } \quad \frac{y d}{D} =(\frac{\mu _g}{\mu _m}-1 )t $
$\therefore \quad y =(\frac{\mu _g}{\mu _m}-1) t \frac{D}{d}$
Substituting the values, we have
$ \begin{aligned} & y=(\frac{1.5}{4 / 3}-1) \frac{10.4 \times 10^{-6}(1.5)}{0.45 \times 10^{-3}} \\ & y=4.33 \times 10^{-3} m \end{aligned} $
or we can say $y=4.33$ $ mm$.
(b) At $O, \Delta x _1=0$ and $\Delta x _2=(\frac{\mu _g}{\mu _m}-1 )t$
$\therefore$ Net path difference, $\Delta x=\Delta x _2$
Corresponding phase difference, $\Delta \phi$
or $\quad$ simple $\phi=\frac{2 \pi}{\lambda} . \Delta x$
Substituting the values, we have
$ \begin{aligned} \phi & =\frac{2 \pi}{6 \times 10^{-7}} (\frac{1.5}{4 / 3}-1)\left(10.4 \times 10^{-6}\right) \\ \phi & =(\frac{13}{3}) \pi \end{aligned} $
$ \begin{aligned} \text { Now, } \quad I(\phi) & =I _{\max } \cos ^{2} (\frac{\phi}{2}) \\ \therefore \quad I & =I _{\max } \cos ^{2} (\frac{13 \pi}{6}) \\ I & =\frac{3}{4} I _{\max } \end{aligned} $
(c) At $O$, path difference is $\Delta x=\Delta x _2=(\frac{\mu _g}{\mu _m}-1 )t$
For maximum intensity at $O$
$ \begin{aligned} \Delta x & =n \lambda \\ \therefore \quad \lambda & =\frac{\Delta x}{1}, \frac{\Delta x}{2}, \frac{\Delta x}{3} \ldots \text { and so on } \\ \Delta x & =(\frac{1.5}{4 / 3}-1)\left(10.4 \times 10^{-6} m\right) \\ & =(\frac{1.5}{4 / 3}-1)\left(10.4 \times 10^{3} nm\right) \end{aligned} $
$\Delta x=1300 $ $nm$
$\therefore \quad$ Maximum intensity will be corresponding to
$ \begin{aligned} \lambda & =1300 nm, \frac{1300}{2} nm, \frac{1300}{3} nm, \frac{1300}{4} nm \ldots \\ & =1300 nm, 650 nm, 433.33 nm, 325 nm \ldots \end{aligned} $
The wavelengths in the range $400$ to $700 $ $nm$ are $650 $ $nm$ and $433.33 $ $nm$.





