Heron's Formula
Multiple Choice Questions(MCQs)
1. An isosceles right triangle has area $8 ~cm^{2}$. The length of its hypotenuse is
(A) $\sqrt{32} ~cm$
(B) $\sqrt{16} ~cm$
(C) $\sqrt{48} ~cm$
(D) $\sqrt{24} ~cm$
Show Answer
Solution
Given: An isosceles right triangle has area $8 ~cm^{2}$.
Area of an isosceles right triangle $=\dfrac{1}{2} \times$ Base $\times$ Height
So, $8=\dfrac{1}{2} \times$ Base $\times$ Height
$(\text{ Base })^{2}=16 \quad$ [Base $=$ height, as triangle is an isosceles]
Base $=\sqrt{16}$
Base $=4 ~cm$
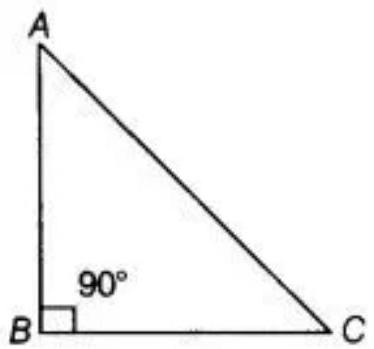
See the triangle $ABC$, using Pythagoras theorem:
$ \begin{aligned} A C^{2}+A B^{2}+B C^{2} & =4^{2}+4^{2} \\ & =16+16 \\ A C^{2} & =32 \\ A C & =\sqrt{32} \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the length of its hypotenuse is $\sqrt{32}$.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
2. The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is $60 m$. The area is
(A) $10 \sqrt{3} m^{2}$
(B) $15 \sqrt{3} m^{2}$
(C) $20 \sqrt{3} m^{2}$
(D) $100 \sqrt{3} m^{2}$
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is $60 m$.
Suppose that each side of an equilateral be a.
$a+a+a=60 m$
$3 a=60 m$
$a=20 m$
Area of an equilateral triangle $=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times(\text{ Side })^{2}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times(20)^{2} \\ & =100 \sqrt{3} m^{2} \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the area of the triangle is $100 \sqrt{3} m^{2}$.
3. The sides of a triangle are $56 ~cm, 60 ~cm$ and $52 ~cm$ long. Then the area of the triangle is
(A) $1322 ~cm^{2}$
(B) $1311 ~cm^{2}$
(C) $1344 ~cm^{2}$
(D) $1392 ~cm^{2}$
Show Answer
Solution
The sides of a triangle are $a=56 ~cm, b=60 ~cm$ and $c=52 ~cm$.
So, semi-perimeter of a triangle will be:
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{56+60+52}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{168}{2} \\ & =84 ~cm \end{aligned} $
Area of the triangle $=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \quad$ [By heron’s formula]
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{84(84-56)(84-60)(84-52)} \\ & =\sqrt{84 \times 28 \times 24 \times 32} \\ & =\sqrt{4 \times 7 \times 3 \times 4 \times 7 \times 4 \times 2 \times 3 \times 4 \times 4 \times 2} \\ & =\sqrt{4^{6} \times 7^{2} \times 3^{2}} \\ & =4^{3} \times 7 \times 3 \\ & =1344 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Hence, the correct option is (C).
4. The area of an equilateral triangle with side $2 \sqrt{3} ~cm$ is
(A) $5.196 ~cm^{2}$
(B) $0.866 ~cm^{2}$
(C) $3.496 ~cm^{2}$
(D) $1.732 ~cm^{2}$
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The side of an equilateral triangle is $2 \sqrt{3} ~cm$.
Now, area of an equilateral triangle $=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}(\text{ Side })^{2}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times(2 \sqrt{3})^{2} \\ & =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times 4 \times 3 \\ & =3 \sqrt{3} \\ & =3 \times 1.732 \\ & =5.196 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Hence, the area of an equilateral triangle is $5.196 ~cm^{2}$.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
5. The length of each side of an equilateral triangle having an area of $9 \sqrt{3} ~cm^{2}$ is
(A) $8 ~cm$
(B) $36 ~cm$
(C) $4 ~cm$
(D) $6 ~cm$
Show Answer
Solution
Given: area of an equilateral triangle $=9 \sqrt{3} ~cm^{2}$
Area of an equilateral triangle $=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times(\text{ Side })^{2}$
$ \begin{aligned} \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times(\text{ Side })^{2} & =9 \sqrt{3} \\ (\text{ Side })^{2} & =9 \times 4 \\ \text{ Side } & =\sqrt{9 \times 4} \\ \text{ Side } & =3 \times 2 \\ \text{ Side } & =6 ~cm \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the length of an equilateral triangle is $6 ~cm$.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
6. If the area of an equilateral triangle is $16 \sqrt{3} ~cm^{2}$, then the perimeter of the triangle is
(A) $48 ~cm$
(B) $24 ~cm$
(C) $12 ~cm$
(D) $306 ~cm$
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The area of an equilateral triangle is $16 \sqrt{3} ~cm^{2}$.
Area of equilateral triangle $=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times(\text{ side })^{2}$
$ \begin{aligned} 16 \sqrt{3} & =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times(\text{ side })^{2} \\ (\text{ Side })^{2} & =\dfrac{16 \sqrt{3} \times 4}{\sqrt{3}} \\ & =64 \end{aligned} $
$ \begin{aligned} & \text{ Side }=\sqrt{64} \\ & \text{ Side }=8 ~cm \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the perimeter of triangle $8+8+8=24 ~cm$
Hence, the correct option is (B).
7. The sides of a triangle are $35 ~cm, 54 ~cm$ and $61 ~cm$, respectively. The length of its longest altitude
(A) $16 \sqrt{5} ~cm$
(B) $10 \sqrt{5} ~cm$
(C) $24 \sqrt{5} ~cm$
(D) $28 ~cm$
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The sides of a triangle are $a=35 ~cm, b=54 ~cm$ and $c=61 ~cm$, respectively. So, semiperimeter of a triangle is:
$s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}=\dfrac{35+54+61}{2}=\dfrac{150}{2}=75$
Area of triangle $=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{75(75-35)(75-54)(75-61)} \\ & =\sqrt{75 \times 40 \times 21 \times 14} \\ & =\sqrt{5 \times 5 \times 3 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5 \times 3 \times 7 \times 7 \times 2} \\ & =5 \times 3 \times 2 \times 2 \times 7 \sqrt{5} \\ & =420 \sqrt{5} \end{aligned} $
As know that,
Area of triangle $ABC=\dfrac{1}{2} \times$ Base $\times$ Altitude
$ \begin{aligned} \dfrac{1}{2} \times 35 \times \text{ Altitude } & =420 \sqrt{5} \\ \text{ Altitude } & =\dfrac{420 \sqrt{5} \times 2}{35} \\ \text{ Altitude } & =24 \sqrt{5} \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the length of altitude is $24 \sqrt{5}$.
Hence, the correct option is $(C)$.
8. The area of an isosceles triangle having base $2 ~cm$ and the length of one of the equal sides $4 ~cm$, is
(A) $\sqrt{15} ~cm^{2}$
(B) $\sqrt{\dfrac{15}{2}} ~cm^{2}$
(C) $2 \sqrt{15} ~cm^{2}$
(D) $4 \sqrt{15} ~cm^{2}$
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The length of side be $a=2 ~cm$ and $b=4 ~cm$.
As we know that,
Area of an isosceles triangle $=\dfrac{a}{4} \sqrt{4 b^{2}-a^{2}}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{2 \sqrt{4 \times(4)^{2}-2^{2}}}{4} \\ & =\dfrac{\sqrt{64-4}}{2} \end{aligned} $
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{\sqrt{60}}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{2 \sqrt{15}}{2} \\ & =\sqrt{15} ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Hence, the correct option is (A).
9. The edges of a triangular board are $6 ~cm, 8 ~cm$ and $10 ~cm$. The cost of painting it at the rate of 9 paise per $~cm^{2}$ is
(A) Rs 2.00
(B) Rs 2.16
(C) Rs 2.48
(D) Rs 3.00
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The edges of a triangular board are $a=6 ~cm, b=8 ~cm$ and $c=10 ~cm$.
Now, semi-perimeter of a triangular board will be:
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{6+8+10}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{24}{2} \\ & =12 ~cm \end{aligned} $
Now, by Heron’s formula:
Area of a triangle board $=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{12(12-6)(12-8)(12-10)} \\ & =\sqrt{12 \times 6 \times 4 \times 2} \\ & =\sqrt{12^{2} \times 2^{2}} \\ & =12 \times 2 \\ & =24 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
As, the cost of painting for area $1 ~cm^{2}=$ Rs. 0.09
So, Cost of paint for area $24 ~cm^{2}=0.09 \times 24=$ Rs. 2.16
Therefore, the cost of a triangular board is Rs. 2.16.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Short Answer Questions with Reasoning
Write True or False and justify your answer:
1. The area of a triangle with base $4 ~cm$ and height $6 ~cm$ is $24 ~cm^{2}$.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The base and height of a triangle are $4 ~cm$ and $6 ~cm$ respectively.
As we know that, area of a triangle $=\dfrac{1}{2} \times$ Base $\times$ Height
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 6 \\ & =12 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Hence, the given statement is false.
2. The area of $\triangle ABC$ is $8 ~ c m^{2}$ in which $A B=A C=4 ~ c m$ and $\angle A=90^{\circ}$.
Show Answer
Solution
Area of a triangle $=\dfrac{1}{2} \times$ Base $\times$ Height
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 4 \\ & =8 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Hence, the given statement is true.
3. The area of the isosceles triangle is $\dfrac{5}{4} \sqrt{11} ~cm^{2}$, if the perimeter is $11 ~cm$ and the base is $5 ~ c m$.
Show Answer
Solution
Suppose that side of isosceles triangle be a.
Now, perimeter of an isosceles triangle:
$2 s=5+a+a[2 s=a+b+c]$
$11=5+2 a$
$2 a=11-5$
$2 a=6$
$a=3$
Now, the formula of an area of isosceles triangle $=\dfrac{a}{4} \sqrt{4 b^{2}-a^{2}}$
So, area of an isosceles triangle $=\dfrac{5 \sqrt{4 \times(3)^{2}-(5)^{2}}}{4}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{5 \sqrt{4 \times 9-25}}{4} \\ & =5 \times \dfrac{\sqrt{36-25}}{4} \\ & =\dfrac{5 \sqrt{11}}{4} ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Hence, the given statement is true.
4. The area of the equilateral triangle is $20 \sqrt{3} ~cm^{2}$ whose each side is $8 ~ cm$.
Show Answer
Solution
Given, side of an equilateral triangle be $8 ~cm$.
Area of the equilateral triangle $=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}(\text{ Side })^{2}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times(8)^{2} \\ & =\dfrac{64}{3} \sqrt{ } 3[\therefore \text{ side }=8 ~cm] \\ & =16 \sqrt{3} ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Hence, the given statement is false.
5. If the side of a rhombus is $10 ~cm$ and one diagonal is $16 ~cm$, the area of the rhombus is $96 ~cm^{2}$.
Show Answer
Solution
Let $PQRS$ be the rhombus whose one diagonal is $16 ~cm$, the area of the rhombus is $10 ~cm$.
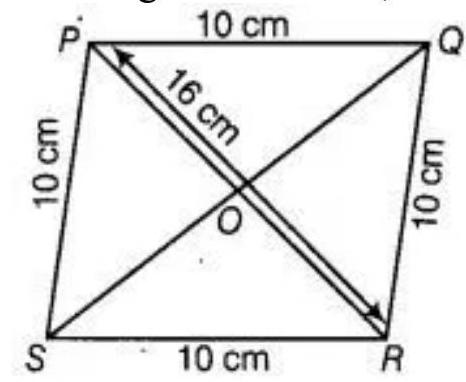
As we know that diagonal of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles. So, $OA=OC=8 ~cm$ and $OB=OD$
Now, in triangle $AOB, \angle A O B=90^{\circ}$
So, $A B^{2}=O A^{2}+O B^{2}$
[By Pythagoras theorem]
$ \begin{aligned} A B^{2} & =O A^{2}+O B^{2} \\ O B^{2} & =A B^{2}-O A^{2} \\ & =(10)^{2}-8^{2} \\ & =100-64 \\ & =36 \end{aligned} $
So, $O B=\sqrt{36}=6$
Also,
$ \begin{aligned} O B & =2(O A)=2 \times 6 \\ & =12 ~cm \end{aligned} $
Therefore, area of rhombus $=\dfrac{1}{2} \times$ Products of diagonals
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times 16 \times 12 \\ & =96 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Hence, the given statement is true.
6. The base and the corresponding altitude of a parallelogram are $10 ~cm$ and $3.5 ~cm$, respectively. The area of the parallelogram is $30 ~cm^{2}$.
Show Answer
Solution
Given, parallelogram in which base $=10 ~cm$ and altitude $=3.5 ~cm$
Area of a parallelogram $=$ Base $x$ Altitude
$ \begin{aligned} & =10 \times 3.5 \\ & =35 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Hence, the given statement is false.
7. The area of a regular hexagon of side ’ $a$ ’ is the sum of the areas of the five equilateral triangles with side $a$.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The side of a regular hexagon is ’ $a$ ‘.
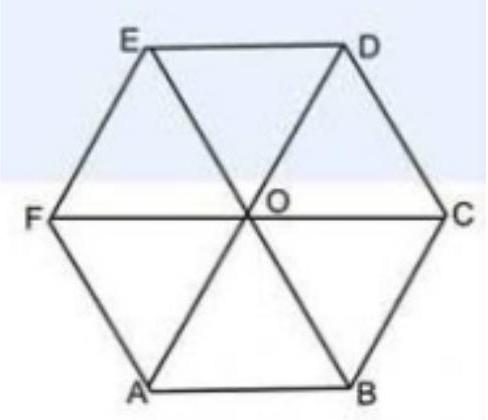
As we know that the regular hexagon is divided into six equilateral triangles. So,
Area of regular hexagon $=$ Sum of area of the six equilateral triangles.
Hence, the given statement is false.
8. The cost of levelling the ground in the form of a triangle having the sides $51 m, 37 m$ and $20 m$ at the rate of $Rs 3$ per $m^{2}$ is $Rs 918$.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The sides of the ground are $a=51 m, b=37 ~cm$, and $c=20 ~cm$. Now, the semiparameter(s) of ground is:
$2 s=a+b+c$
$2 s=51 m+37 m+20 m$
$2 s=108 m$
$s=\dfrac{108 m}{2}$
$s=54 m$
Area of triangle $=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{54(54-51)(54-37)(54-20)} \\ & =\sqrt{54 \times 3 \times 17 \times 34} \\ & =\sqrt{3 \times 3 \times 3 \times 2 \times 3 \times 17 \times 17 \times 2} \\ & =3 \times 3 \times 17 \times 2 \\ & =306 m^{2} \end{aligned} $
The cost of levelling of $1 m^{2}$ area is Rs. 3 .
So, cost of levelling the ground of $306 m^{2}$ area = Rs. $3 \times 306=$ Rs. 918
Hence, the given statement is true.
9. In a triangle, the sides are given as $11 ~cm, 12 ~cm$ and $13 ~cm$. The length of the altitude is $10.25 ~cm$ corresponding to the side having length $12 ~cm$.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The length of the altitude is 10.25 . And in a triangle, the sides are $a=11 ~cm, b=12 ~cm$ and $c=13 ~cm$.
So, semi-perimeter(s) will be:
$2 s=a+b+c$
$2 s=11 ~cm+12 ~cm+13 ~cm$
$2 s=36 ~cm$
$s=\dfrac{36}{2}$
$s=18 ~cm$
So, area of triangle $=\dfrac{2 \times \text{ Area of } \Delta}{\text{ Base }}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{2 \times 6 \sqrt{105}}{12} \\ & =\sqrt{105} \\ & =10.25 \end{aligned} $
Hence, the given statement is true.
Short Answer Questions
1. Find the cost of laying grass in a triangular field of sides $50 m, 65 m$ and $65 m$ at the rate of $Rs 7$ per $m^{2}$.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The sides of the ground are $a=50 m, b=65 m$, and $c=65 m$. Now, the semiparameter(s) of the cost of levelling is:
$2 s=a+b+c$
$2 s=50 m+65 m+65 m$
$2 s=180 m$
$s=\dfrac{180 m}{2}$
$s=90 m$
Area of triangle $=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{90(90-50)(90-65)(90-65)} \\ & =\sqrt{90 \times 40 \times 25 \times 25} \\ & =3 \times 2 \times 10 \times 25 \\ & =6 \times 250 \\ & =1500 m^{2} \end{aligned} $
The cost of laying grass $1 m^{2}$ area is Rs. 7 .
Therefore, the cost of levelling grass per $1500 m^{2}=$ Rs. $7 \times 1500=$ Rs. 10500
2. The triangular side walls of a flyover have been used for advertisements. The sides of the walls are $13 m, 14 m$ and $15 m$. The advertisements yield an earning of $Rs 2000$ per $m^{2}$ a year. A company hired one of its walls for 6 months. How much rent did it pay?
Show Answer
Solution
Let the sides of a triangular walls are $a=13 m, b=14 m$ and $c=15 m$.
Now, the semi-perimeter of triangular side wall,
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{13+14+15}{2} \\ & =21 m \end{aligned} $
Now, area of triangular wall $=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$ [By Heron’s formula]
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{21(21-13)(21-14)(21-15)} \\ & =\sqrt{21 \times(21-13) \times(21-14) \times(21-15)} \\ & =\sqrt{21 \times 8 \times 7 \times 6} \\ & =\sqrt{21 \times 4 \times 2 \times 7 \times 3 \times 2} \\ & =\sqrt{21^{2} \times 4^{2}} \\ & =21 \times 4 \\ & =84 m^{2} \end{aligned} $
The advertisement yield earning per year for $1 m^{2}$ area is Rs. 2000 .
Therefore, advertisement yield earning per year on $84 m^{2}=2000 \times 84=$ Rs. 168000 .
According to the question, the company hired one of its walls for 6 months, therefor company pay the rent $=\dfrac{1}{2} \times 168000=$ Rs. 84000 .
Hence, the company paid rent Rs. 84000 .
3. From a point in the interior of an equilateral triangle, perpendiculars are drawn on the three sides. The lengths of the perpendiculars are $14 ~cm, 10$ $~cm$ and $6 ~cm$. Find the area of the triangle.
Show Answer
Solution
Let $ABC$ be an equilateral triangle, $O$ be the interior point and $OP=14 ~cm, OQ=10 ~cm$ and $OR=6 ~cm$. Also, sides of an equilateral triangle be $a m$.
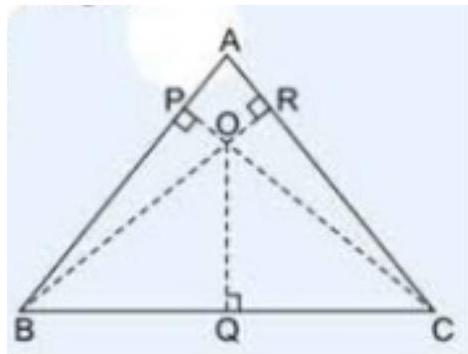
Area of triangle $OAB=\dfrac{1}{2} \times A B \times O P[.$ Area of a triangle $=\dfrac{1}{2} \times($ Base $\times$ Height $.)]$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times a \times 14 \\ & =7 a ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Similarly, Area of triangle $OBC=\dfrac{1}{2} \times B C \times O Q$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times a \times 10 \\ & =5 a ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Again, area of triangle $OAC=\dfrac{1}{2} \times A C \times O R$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times a \times 6 \\ & =3 a ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
See the given figure, area of equilateral triangle $ABC=$ Area of $(\triangle O A B+\triangle O B C+\triangle O A C)$
$=(7 a+5 a+3 a) ~cm^{2}$
$=15 a ~cm^{2}$
Now, semi-perimeter of triangle $ABC$ is:
$s=\dfrac{a+a+a}{2}$
$s=\dfrac{3 a}{2} ~cm$
As, area of equilateral triangle $ABC=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \quad$ [By Heron’s formula]
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{\dfrac{3 a}{2}(\dfrac{3 a}{2}-a)(\dfrac{3 a}{2}-a)(\dfrac{3 a}{2}-a)} \\ & =\sqrt{\dfrac{3 a}{2} \times \dfrac{a}{2} \times \dfrac{a}{2} \times \dfrac{a}{2}} \\ & =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^{2} \ldots \text{ (II) } \end{aligned} $
According to the equation (I) and (II), get:
$ \begin{aligned} \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^{2} & =15 a \\ a & =\dfrac{15 \times 4}{\sqrt{3}} \\ a & =\dfrac{60}{\sqrt{3}} \\ a & =20 \sqrt{3} \end{aligned} $
Putting $a=20 \sqrt{3}$ in equation (II), get:
Area of triangle $ABC=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times(20 \sqrt{3})^{2}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times 400 \times 3 \\ & =300 \sqrt{3} ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Hence, the area of an equilateral triangle is $300 \sqrt{3} ~cm^{2}$.
4. The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is $32 ~cm$. The ratio of the equal side to its base is $3: 2$. Find the area of the triangle.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: Perimeter of triangle $=32 ~cm$
The ratio of the equal side to its base of an isosceles triangle is $3: 2$. Let sides of an isosceles triangle be $3 x, 3 x$ and $2 x$.
So, perimeter of the triangle $=3 x+3 x+2 x=8 x$
$32=8 x$
$x=\dfrac{32}{8}$
$x=4$
Since, the sides of the isosceles triangle are $3 \times 4=12,3 \times 4=12$ and $2 \times 4=8 ~cm$.
Now, semi-perimeter of triangle will be:
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{12+12+8}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{32}{2} \\ & =16 ~cm \end{aligned} $
Area of triangle $=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{16(16-12)(16-12)(16-8)} \\ & =\sqrt{16 \times 4 \times 4 \times 8} \\ & =4 \times 4 \times 2 \sqrt{2} ~cm^{2} \\ & =32 \sqrt{2} \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the area of an isosceles triangle $ABC=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{16(16-12)(16-12)(16-8)} \\ & =\sqrt{16 \times 4 \times 4 \times 8} \\ & =32 \sqrt{2} ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the area of an isosceles triangle is $32 \sqrt{2} ~cm^{2}$.
5. Find the area of a parallelogram given in Fig. Also find the length of the altitude from vertex $A$ on the side DC.
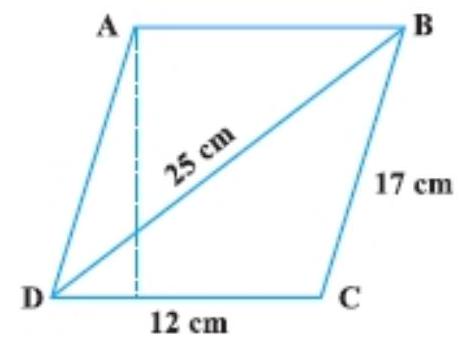
Show Answer
Solution
Let the sides of a triangle $BCD$ are $a=12 ~cm, b=17 ~cm$ and $c=25 ~cm$ and altitude of $a$ parallelogram is $h$.
Area of parallelogram, $ABCD=2$ (Area of triangle BCD)
Now, semi-perimeter(s) of triangle BCD will be:
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{12+17+25}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{54}{2} \\ & =27 ~cm \end{aligned} $
Area of triangle $BCD=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \quad$ [By heron’s formula]
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{27(27-12)(27-17)(27-25)} \\ & =\sqrt{27 \times 15 \times 10 \times 2} \\ & =\sqrt{9 \times 3 \times 3 \times 5 \times 5 \times 2 \times 2} \\ & =3 \times 3 \times 5 \times 2 ~cm^{2} \\ & =90 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
So, area of parallelogram $ABCD=2 \times$ Area of triangle $BCD$
$$ \begin{align*} & =2 \times 90 ~cm^{2} \\ & =180 ~cm^{2} \tag{II} \end{align*} $$
As, Area of parallelogram $ABCD=$ Base $\times$ Altitude
$ \begin{aligned} 180 & =DC \times h \\ 180 & =12 \times h \\ h & =\dfrac{180}{12} \\ h & =15 ~cm \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the area of parallelogram is $180 ~cm^{2}$ and the length of altitude is $15 ~cm$.
6. A field in the form of a parallelogram has sides $60 m$ and $40 m$ and one of its diagonals is $80 m$ long. Find the area of the parallelogram.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: Let a field in the form of a parallelogram $A B C D$ has sides $60 m$ and $40 m$ and one of its diagonals is $80 m$ long.
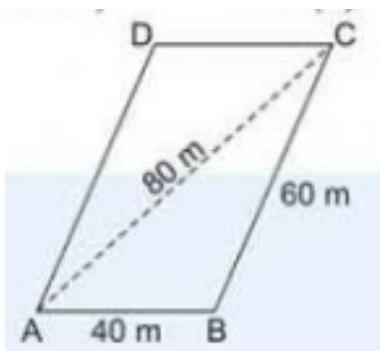
See the figure, in triangle $A B C$, let $a=40 m, b=60 m$ and $c=80 m$.
Now, semi perimeter(s) of triangle $ABC$ :
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{40+60+80}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{180}{2} \\ & =90 m \end{aligned} $
So, area of triangle $ABC$ will be $=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{90(90-40)(90-60)(90-80)} \\ & =\sqrt{90 \times 50 \times 30 \times 10} \\ & =\sqrt{3 \times 30 \times 5 \times 10 \times 30 \times 10} \\ & =300 \sqrt{15} \\ & =1161.895 m^{2} \end{aligned} $
Now, from equation (I),
Area of parallelogram $ABCD=2 \times 1161.895 m^{2}=2323.79 m^{2}$.
Therefore, the area of parallelogram ABCD is $2323.79 m^{2}$.
7. The perimeter of a triangular field is $420 m$ and its sides are in the ratio 6 $: 7: 8$. Find the area of the triangular field.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The perimeter of a triangular field is $420 m$ and its sides are in the ratio $6: 7: 8$.
According to the question, Let the sides in meters are $a=6 x, b=7 x$ and $c=8 x$.
So, perimeter of the triangle $=6 x+7 x+8 x$
$420=21 x$ $x=\dfrac{420}{21}$
$x=20$
Since, the sides of the triangular field are $a=6 \times 20 ~cm=120 m, b=7 \times 20 m=140 m$ and $c=8 \times 20 m=160 m$.
Now, semi-perimeter(s) of triangle will be:
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times 420 m \\ & =210 m \end{aligned} $
Area of the triangle field $=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$ [Using Heron’s formula]
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{210(210-120)(210-140)(210-160)} \\ & =\sqrt{210 \times 90 \times 70 \times 50} \\ & =100 \sqrt{7 \times 3 \times 3^{2} \times 7 \times 5} \\ & =100 \times 7 \times 3 \times \sqrt{15} \\ & =2100 \sqrt{15} \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the area of the triangular field is $2100 \sqrt{15}$.
8. The sides of a quadrilateral $A B C D$ are $6 ~cm, 8 ~cm, 12 ~cm$ and $14 ~cm$ (taken in order) respectively, and the angle between the first two sides is a right angle. Find its area.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: The sides of a quadrilateral $ABCD$ are $AB=6 ~cm, BC=8 ~cm$, and $CD=12 ~cm$ and $DA=14 ~cm$.
Construction: Join AC.
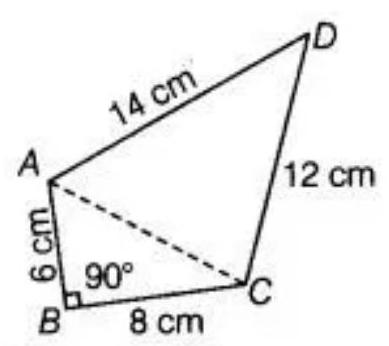
In the right triangle $ABC$, whose angle $B$ is right angle. So, $A C^{2}=A B^{2}+B C^{2}$ [By Pythagoras theorem]
$A C^{2}=6^{2}+8^{2}$
$A C^{2}=36+64$
$A C=\sqrt{100}$
$A C=10$
Area of quadrilateral $ABCD=$ Area of triangle $ABC+$ Area of triangle $ACD$
Now, area of triangle $ABC=\dfrac{1}{2} \times A B \times A C$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 8 \\ & =24 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
In triangle $A C D$, let $A C=a=10 ~cm, C D=b=12 ~cm$, and $D A=c=14 ~cm$.
Now, semi-perimeter of triangle ACD will be:
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{10+12+14}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{36}{2} \\ & =18 ~cm \end{aligned} $
So, area of triangle $ACD=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$ [By heron’s formula]
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{18(18-10)(18-12)(18-14)} \\ & =\sqrt{18 \times 8 \times 6 \times 4} \\ & =\sqrt{(3)^{2} \times 2 \times 4 \times 2 \times 3 \times 2 \times 4} \\ & =3 \times 4 \times 2 \sqrt{3 \times 2} \\ & =24 \sqrt{6} ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Hence, the area of the quadrilateral $ABCD$ is $24 \sqrt{6} ~cm^{2}$.
9. A rhombus shaped sheet with perimeter $40 ~cm$ and one diagonal $12 ~cm$, is painted on both sides at the rate of $Rs 5$ per $m^{2}$. Find the cost of painting.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: One diagonal $=12 ~cm$, Perimeter of rhombus $=40 ~cm$
So,
$4 \times$ Side $=40$
side $=\dfrac{40}{4}$
Side $=10 ~cm$
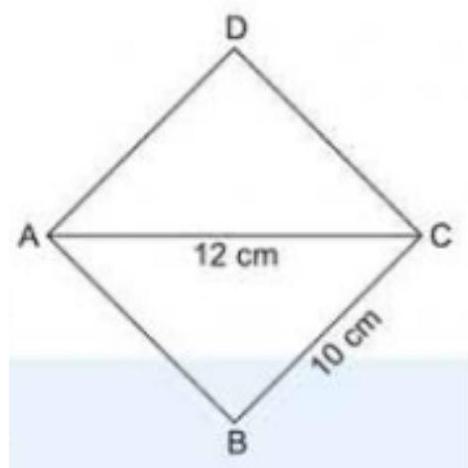
In triangle $A B C$, let $a=10 ~cm, b=10 ~cm$, and $c=12 ~cm$.
As we know that rhombus is also a parallelogram, so its diagonal divide it into two congruent triangles of equal area. So,
Area of rhombus $=2($ Area of triangle ABC)
Now, Semi-perimeter of triangle $ABC$ will be:
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{10+10+12}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{32}{2} \\ & =16 ~cm \end{aligned} $
So, area of triangle $ABC=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{16(16-10)(16-10)(16-12)} \\ & =\sqrt{16 \times 6 \times 6 \times 4} \\ & =\sqrt{2304} \\ & =48 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Since, area of rhombus $=2$ (Area of triangle $ABC)$
$ \begin{aligned} & =2 \times 48 ~cm^{2} \\ & =96 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
The cost of painting of the sheet is Rs. 5 per $m^{2}$.
Therefore, cost of painting both sides of rhombus shaped sheet $ABCD=$ Rs. $(2 \times 5 \times 96)=$ Rs. 960 .
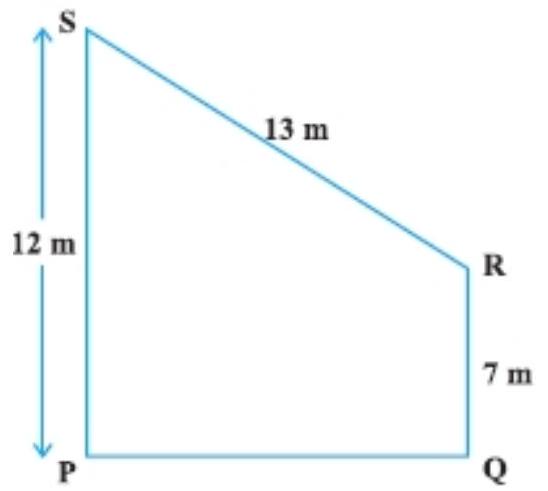
10. Find the area of the trapezium PQRS with height $P Q$ given in Fig.
Show Answer
Solution
Let PQRS is a trapezium, in which draw a line RT perpendicular to PS.
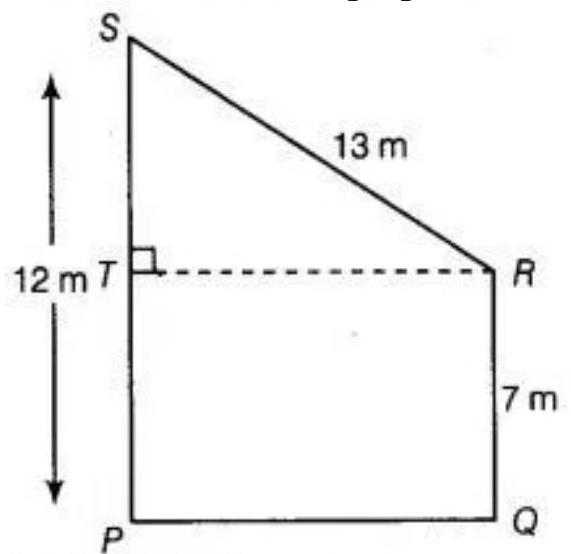
See the figure, $ST=PS-TP=12-7=5 ~cm$
So, in right triangle STR,
$(S R)^{2}=(S T)^{2}+(T R)^{2}$ [By using Pythagoras theorem]
$(13)^{2}=(5)^{2}+(T R)^{2}$
$(T R)^{2}=169-25$
$(T R)^{2}=144$
$T R=12 m$
Now, area of triangle STR $=\dfrac{1}{2} \times T R \times T S$ [area of triangle $=\dfrac{1}{2} \times$ Base $\times$ Height
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times 12 \times 5 \\ & =30 m^{2} \end{aligned} $
As, area of rectangle $PQRT=P Q \times R Q=12 \times 7=84 m^{2}$
Now, area of trapezium $=$ Area of DSTR + Area of rectangle PQRT
$ \begin{aligned} & =30+84 \\ & =114 m^{2} \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the area of trapezium is $114 m^{2}$.
Long Answer Questions
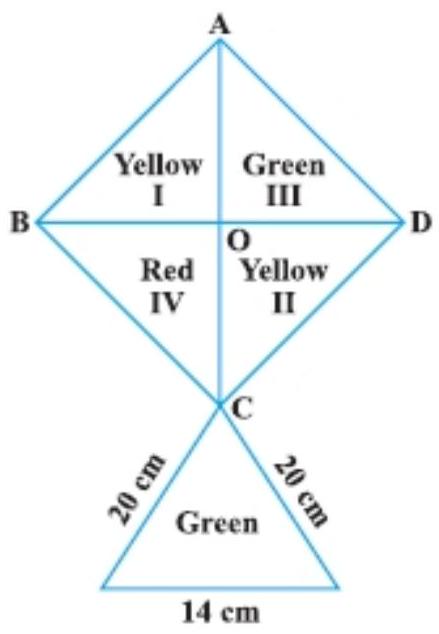
1. How much paper of each shade is needed to make a kite given in Fig., in which $A B C D$ is a square with diagonal $44 ~cm$ ?
Show Answer
Solution
Given: Diagonal of square $ABCD=44 ~cm$
Also, $ABCD$ is a square. $So, AB=BC=CD=DA$
Now, in triangle $A C D$,
$ \begin{aligned} A C^{2} & =A D^{2}+D C^{2} \\ 44^{2} & =A D^{2}+A D^{2} \\ 2 A D^{2} & =44 \times 44 \\ 2 A D^{2} & =22 \times 2 \times 22 \times 2 \\ A D^{2} & =22 \times 2 \times 22 \\ A D & =\sqrt{22 \times 2 \times 22} \\ A D & =22 \sqrt{2} \end{aligned} $
Now, area of square $ABCD=$ Side $\times$ Side $=22 \sqrt{2} \times 22 \sqrt{2}=968 ~cm^{2}$
Since, area of square is divided into four parts.
Now, the area of paper of Red shade needed to make the kite is: $=\dfrac{1}{4} \times 968 ~cm^{2}=242 ~cm^{2}$
Also, area of green portion is:
$=\dfrac{1}{4} \times 968 ~cm^{2}$
$=242 ~cm^{2}$
Similarly, area of yellow portion is:
$ =\dfrac{1}{2} \times 968 ~cm^{2}=484 ~cm^{2} $
In triangle $P C Q$, Let $P C=a=20 ~cm, C Q=b=20 ~cm$, and $P Q=c=14 ~cm$.
Now, semi-perimeter of triangle PCQ will be:
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{20+20+14}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{54}{2} \\ & =27 ~cm \end{aligned} $
So, area of triangle PCQ $=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{27 \times(27-20) \times(27-20)(27-14)} \\ & =\sqrt{27 \times 7 \times 7 \times 13} \\ & =\sqrt{3 \times 3 \times 3 \times 7 \times 7 \times 13} \\ & =21 \sqrt{39} \\ & =21 \times 6.24 \\ & =131.04 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Since, the total area of green portion $=242 ~cm^{2}+131.04 ~cm^{2}=373.04 ~cm^{2}$
Therefore, the paper required for each shade to make a kite is red paper $=242 ~cm^{2}$, yellow paper $=484 ~cm^{2}$, and green paper $=373.04 ~cm^{2}$.
2. The perimeter of a triangle is $50 ~cm$. One side of a triangle is $4 ~ c m$ longer than the smaller side and the third side is $6 ~cm$ less than twice the smaller side. Find the area of the triangle.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: the perimeter of a triangle is $50 ~cm$.
Now, semi-perimeter(s) of the triangle is $=\dfrac{\text{ Perimeter of triangle }}{2}=\dfrac{50}{2}=25$
Suppose that the smaller side of the triangle be $a=x~cm$. So, the second side will $be b=(x+4)$ $~cm$ and $3^{\text{rd }}$ side will be $c=(2 x-6) ~cm$.
Now, perimeter of triangle $=a+b+c=x+(x+4)+(2 x-6)$
$50 ~cm=(4 x-2) ~cm$
$50=4 x-2$
$4 x=50+2$
$4 x=52$
$x=\dfrac{52}{4}$
$x=13$
Since, the three side of the triangle are:
$a=x=13$,
$b=x+4=13+4=17$
$c=2 x-6=2 \times 13-6=26-6=20$.
So, area of the triangle $=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{25 \times(25-13) \times(25-17) \times(25-20)} \\ & =\sqrt{25 \times 12 \times 8 \times 5} \\ & =\sqrt{5 \times 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 4 \times 2 \times 5} \\ & =5 \times 4 \times 20 \sqrt{30} ~cm^{2} \\ & =20 \sqrt{30} ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the area of triangle is $20 \sqrt{30} ~cm^{2}$.
3. The area of a trapezium is $475 ~cm^{2}$ and the height is $19 ~cm$. Find the lengths of its two parallel sides if one side is $4 ~ c m$ greater than the other.
Show Answer
Solution
Given:
Area of a trapezium $=475 ~cm^{2}$ and Height $=19 ~cm$.
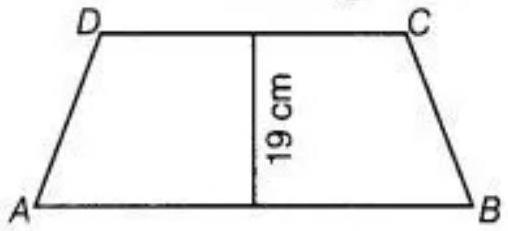
According to the question, let one sides of trapezium is $x$. So, another side will be $x+4$.
Now, Area of trapezium $=\dfrac{1}{2} \times($ Sum of the parallel sides $) \times$ Height
$ \begin{aligned} 475 & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times(x+x+4) \times 19 ~cm \\ 2 x+4 & =\dfrac{950}{19} \\ & =50 \\ 2 x & =50-4 \\ 2 x & =46 \\ x & =23 \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the length of the parallel side of trapezium are $x=23 ~cm$ and $x+4=23+4=27$ $~cm$.
4. A rectangular plot is given for constructing a house, having a measurement of $40 m$ long and $15 m$ in the front. According to the laws, a minimum of $3 m$, wide space should be left in the front and back each and 2 $m$ wide space on each of other sides. Find the largest area where house can be constructed.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: Let a rectangular plot $ABCD$ is constructing a house, having a measurement of $40 m$ long and $15 m$ in the front.
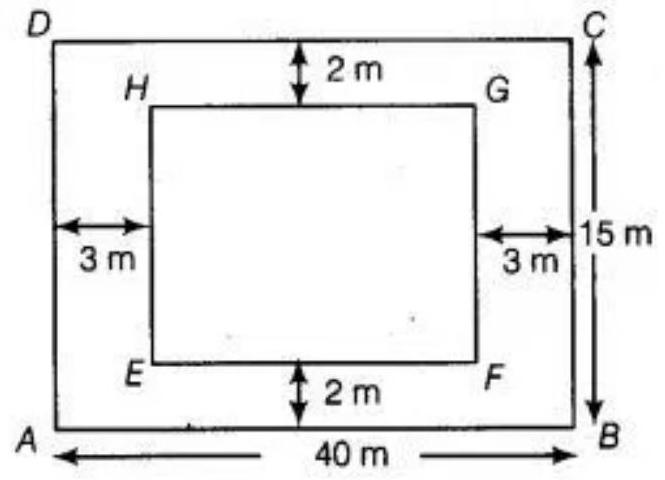
According to the question,
Length of inner-rectangle $(E F)=40-3-3=34 m$
And breadth of inner rectangle $(FG)=15-2-2=11 m$
Now, area of inner rectangle $(EFGH)$ will be $=$ Length $x$ Breadth
$ \begin{aligned} & =E F \times F G \\ & =34 \times 11 m^{2} \\ & =374 m^{2} \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the largest area where house can be constructed $=374 m^{2}$.
5. A field is in the shape of a trapezium having parallel sides $90 m$ and $30 m$. These sides meet the third side at right angles. The length of the fourth side is $100 m$. If it costs $R 4$ to plough $1 m^{2}$ of the field, find the total cost of ploughing the field.
Show Answer
Solution
Given: In the trapezium $ABCD$, the two parallel sides are $AB=90 m, CD=30 m$, and $E C \perp A B$.
So, $EB=AB-EA=90 m-30 m=60 m$
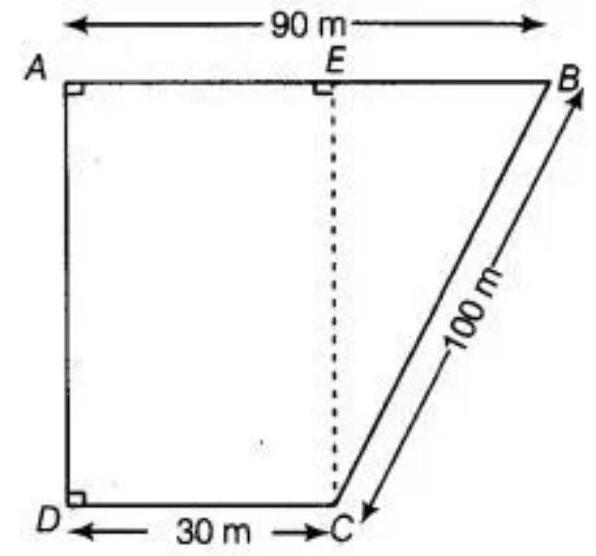
Now, in triangle BEC,
$ \begin{aligned} (B C)^{2} & =(B E)^{2}+(E C)^{2} \\ 100^{2} & =60^{2}+(E C)^{2} \\ (E C)^{2} & =10000-3600 \\ (E C)^{2} & =6400 \\ E C & =\sqrt{6400} \\ E C & =80 m \end{aligned} $
Now, area of trapezium $A B C D=\dfrac{1}{2} \times($ Sum of parallel sides $) \times($ Distance between parallel sides $)$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times(A B+C D) \times E C \\ & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times(90+30) \times 80 \\ & =\dfrac{1}{2} \times 120 \times 80 \\ & =4800 m^{2} \end{aligned} $
The cost of ploughing the field of $1 m^{2}$ is Rs. 4.
Now, The cost of ploughing the field of $4800 m^{2}$ area $=4800 \times$ Rs. $4=$ Rs. 19200 .
Therefore, the total cost of plughing the field is Rs. 19200.
6. In Fig., $\triangle ABC$ has sides $AB=7.5 ~cm, AC=6.5 ~cm$ and $BC=7 ~cm$. On base $B C$ a parallelogram $D B C E$ of same area as that of $\triangle ABC$ is constructed. Find the height DF of the parallelogram.
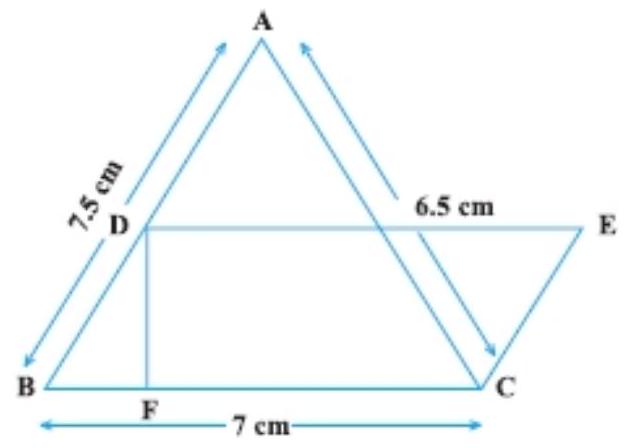
Show Answer
Solution
Given: in triangle $ABC$, the sides are $AB=a=7.5 ~cm, BC=b=7 ~cm$, and $CA=c=6.5 ~cm$. Now, semi-perimeter of a triangle will be:
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{7.5+7+6.5}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{21}{2} \\ & =10.5 \end{aligned} $
So, area of triangle $ABC=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$ [By heron’s formula]
$ \begin{aligned} & =\sqrt{10.5 \times(10.5-7.5)(10.5-7)(10.5-6.5)} \\ & =\sqrt{10.5 \times 3 \times 3.5 \times 4} \\ & =\sqrt{441} \\ & =21 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
Also, the area of parallelogram BCED will be $=$ Base $\times$ Height
$ \begin{aligned} & =B C \times D F \\ & =7 \times D F \end{aligned} $
Now, according to the question,
Area of triangle $ABC=$ Area of parallelogram BCED
$21=7 \times D F$
$D F=\dfrac{21}{4}$
$D F=3 ~cm$
Hence, the height of parallelogram BCED is $3 ~cm$.
7. The dimensions of a rectangle $A B C D$ are $51 ~cm \times 25 ~cm$. A trapezium PQCD with its parallel sides $Q C$ and $P D$ in the ratio $9: 8$, is cut off from the rectangle as shown in the Fig. If the area of the trapezium $PQCD$ is $\dfrac{5}{6}$ th part of the area of the rectangle, find the lengths QC and PD.
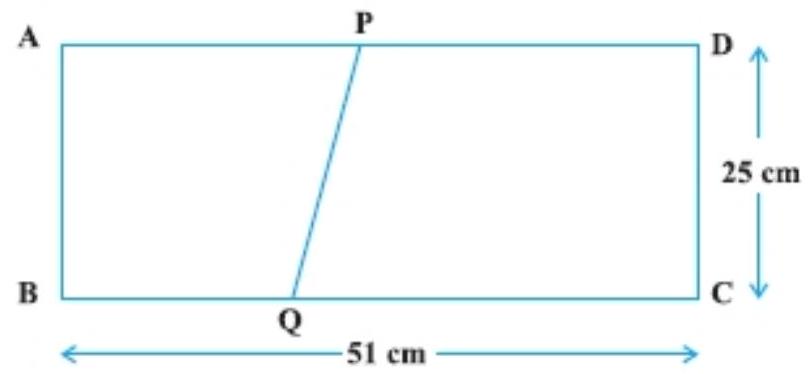
Show Answer
Solution
Given: $A B C D$ is a rectangle, where $A B=51 ~cm$ and $B C=25 ~cm$.
The parallel sides $QC$ and $PD$ of the trapezium $PQCD$ are in the ratio of 9:8. Let $QC=9 x$ and $P D=8 x$.
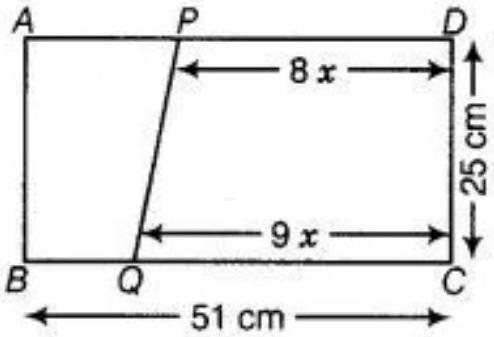
Now, the area of trapezium PQCD:
$=\dfrac{1}{2} \times($ Sum of parallel sides $) \times($ Distance between parallel sides $)$
$=\dfrac{1}{2} \times(9 x+8 x) \times 25 ~cm^{2}$
$=\dfrac{1}{2} \times 17 x \times 25$
Again, area of rectangle $ABCD=B C \times C D=51 \times 25$
Now, according to the question,
Area of trapezium PQCD $=\dfrac{5}{6} \times$ Area of rectangle ABCD
$ \begin{aligned} \dfrac{1}{2} \times 17 x \times 25 & =\dfrac{5}{6} \times 51 \times 25 \\ x & =\dfrac{5}{6} \times 51 \times 25 \times 2 \times \dfrac{1}{17 \times 25} \\ x & =5 \end{aligned} $
Therefore, the length of the trapezium $PQCD, QC=9 x=9 \times 5=45 ~cm$ and, $PD=8 x=$ $8 \times 5=40 ~cm$.
8. A design is made on a rectangular tile of dimensions $50 ~cm \times 70 ~cm$ as shown in Fig. The design shows 8 triangles, each of sides $26 ~cm, 17 ~cm$ and $25 ~cm$. Find the total area of the design and the remaining area of the tile.
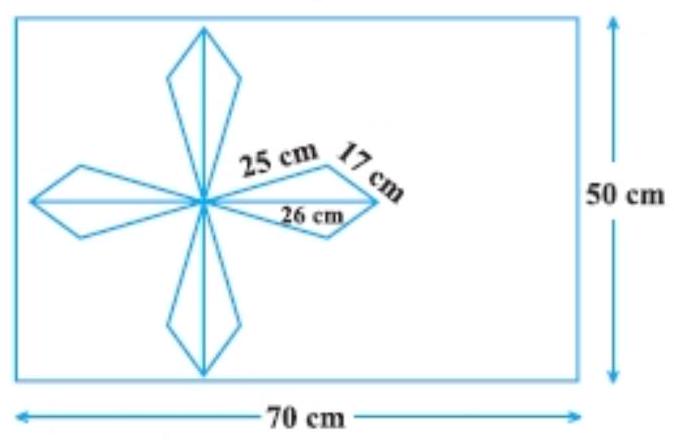
Show Answer
Solution
Given: the dimension of the rectangular tile are $50 ~cm \times 70 ~cm$.
So, area of the rectangular tile $=50 ~cm \times 70 ~cm=3500 ~cm^{2}$.
See the given figure in the question, the sides of the triangle $A B C$ be:
$a=25 ~cm, b=17 ~cm$, and $c=26 ~cm$
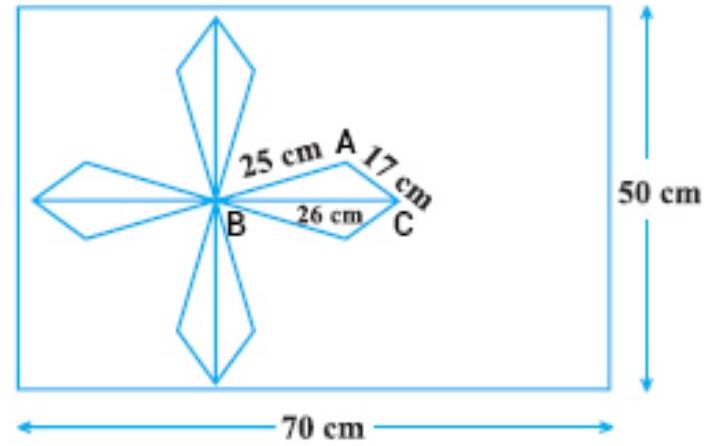
Since, semi-parameter(s) of triangle be:
$ \begin{aligned} s & =\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{25+17+26}{2} \\ & =\dfrac{68}{2} \\ & =34 \end{aligned} $
So, area of triangle $ABC=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
Since, Total area of eight triangle $=8 \times$ Area of triangle $ABC$
$ \begin{aligned} & =204 \times 8 \\ & =1632 ~cm^{2} \end{aligned} $
The area of the design will be equal to the area of eight triangle that is $1632 ~cm^{2}$.
Now, remaining area of the tile $=$ Area of the rectangle - Area of the design $=$ $3500 ~cm^{2}-1632 ~cm^{2}=1868 ~cm^{2}$
Therefore, total area of the design is $1632 ~cm^{2}$ and the remaining area of the tile is $1868 ~cm^{2}$.





