Coordinate Geometry-i Straight Line (Lecture-03)
14. Locus of the image of the point $(2,3)$ in the line $(x-2 y+3)+\lambda(2 x-3 y+4)=0$ is
(a) $x^{2}+y^{2}-3 x-4 y-4=0$
(b) $2 x^{2}+2 y^{2}+2 x+4 y-7=0$
(c) $x^{2}+y^{2}-2 x-4 y+4=0$
(d) None
Show Answer
Solution: $\left.\begin{array}{l}x-2 y+3=0 \\ 2 x-3 y+4=0\end{array}\right\} P(1,2)$
Let image be $\mathrm{B}(\mathrm{h}, \mathrm{k})$ then $\mathrm{AP}=\mathrm{BP}$
$\Rightarrow(\mathrm{h}-1)^{2}+(\mathrm{k}-2)^{2}=1^{2}+1^{2}$
$\mathrm{h}^{2}+\mathrm{k}^{2}-2 \mathrm{~h}-4 \mathrm{k}+5=2$
$\mathrm{x}^{2}+\mathrm{y}^{2}-2 \mathrm{x}-4 \mathrm{y}+3=0$
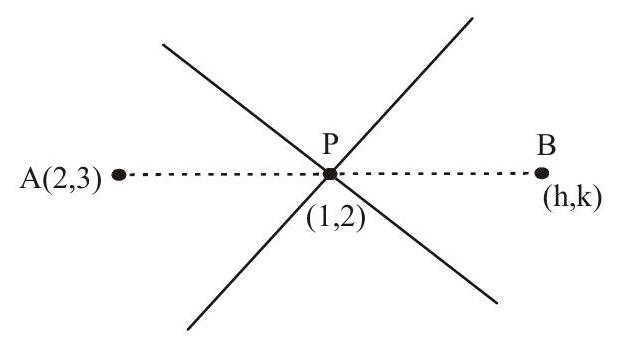
Answer : d
15. If the lines $a x+y+1=0, x+b y+1=0$ and $x+y+c=0 (a, b, c$ being distinct and different from 1$)$ are concurrent, then $\left(\dfrac{1}{1-a}\right)+\dfrac{1}{1-b}+\dfrac{1}{1-c}=$
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) $\dfrac{1}{a+b+c}$
(d) None
Show Answer
Solution:
$\mathrm{c} _{2} \rightarrow \mathrm{c} _{2}-\mathrm{c} _{1}, \mathrm{c} _{3} \rightarrow \mathrm{c} _{3}-\mathrm{c} _{1}$
$\left|\begin{array}{ccc}\mathrm{a} & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & \mathrm{~b} & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & \mathrm{c}\end{array}\right|=0 \Rightarrow\left|\begin{array}{ccc}\mathrm{a} & 1-\mathrm{a} & 1-\mathrm{a} \\ 1 & \mathrm{~b}-1 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 & \mathrm{c}-1\end{array}\right|=0$
$a(b-1)(c-1)-(1-a)(c-1)+(1-a)(1-b)=0$
divide by $(1-a)(1-b)(1-c)$ we get
$\Rightarrow \quad \dfrac{a}{1-a}+\dfrac{1}{1-b}+\dfrac{1}{1-c}=0$
$\Rightarrow \quad \dfrac{1}{1-\mathrm{a}}+\dfrac{1}{1-\mathrm{b}}+\dfrac{1}{1-\mathrm{c}}=1$
16. The set of values of ’ $b$ ’ for which the origin and the point $(1,1)$ lie on the same side of the st. line $\mathrm{a}^{2} \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{aby}+1=0 \quad \forall \mathrm{a} \in \mathrm{R}, \mathrm{b}>\mathrm{o}$ are
(a) $\mathrm{b} \in[2,4)$
(b) $\mathrm{b} \in(0,2)$
(c) $\mathrm{b} \in[0,2]$
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Solution: $(0,0)$ & $(1,1)$ are on the same side
$0+1>0$ so $\mathrm{a}^{2}+\mathrm{ab}+1>0$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{D}<0$ i.e
$b^{2}-4<0$
$b^{2}<4$
$-2<b<2$ but $b>0$
$\therefore \mathrm{b} \in(0,2)$
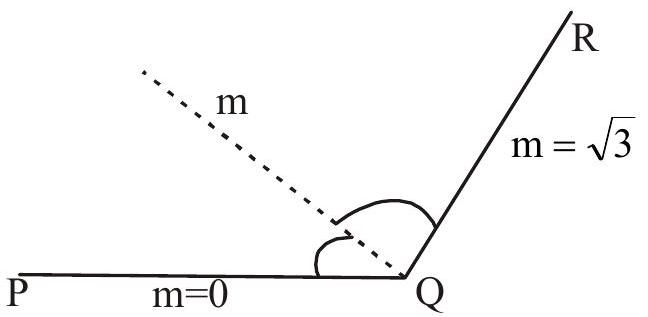
17. Let $P(-1,0), Q(0,0)$ and $R(3,3 \sqrt{3})$ be three points. Then the equation of the bisector of the angle $\mathrm{PQR}$ is
(a) $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y}=0$
(b) $x+\sqrt{3} y=0$
(c) $\sqrt{3} \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y}=0$
(d) $x+\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} y=0$
Show Answer
Solution:
$\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-m}{1+\sqrt{3 m}}=\dfrac{m}{1+0}$
$\begin{aligned} \sqrt{3}-m=m+\sqrt{3} m^{2} \Rightarrow & \sqrt{3} m^{2}+2 m-\sqrt{3}=0 \\ & \sqrt{3} m^{2}+3 m-m-\sqrt{3}=0 \\ & (\sqrt{3} m-1)(3+\sqrt{3})=0 \\ & m=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}},-\sqrt{3} \end{aligned}$
$y=-\sqrt{3} \mathrm{x}$
$\sqrt{3} x+y=0$
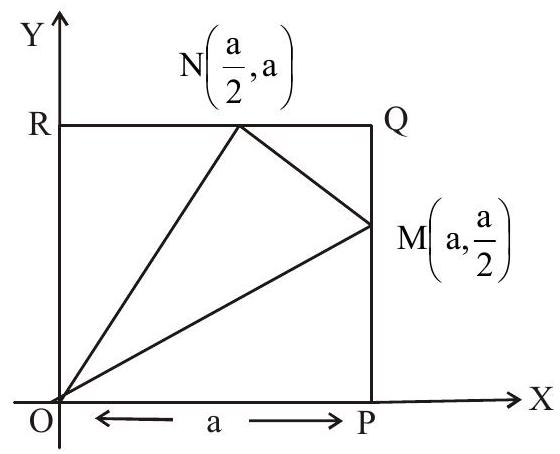
18. $\mathrm{OPQR}$ is a square and $\mathrm{M}, \mathrm{N}$ are the mid points of the sides $\mathrm{PQ}$ and $\mathrm{QR}$ respectively. If the ratio of the areas of the square and the triangle OMN is $\lambda: 6$, then $\dfrac{\lambda}{4}$ is equal to
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 12
(d) 16
Show Answer
Solution: ar. of square $=a^{2}$
ar of $\Delta \mathrm{OMN}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left|\begin{array}{lll}0 & 0 & 1 \\ \mathrm{a} & \dfrac{\mathrm{a}}{2} & 1 \\ \dfrac{\mathrm{a}}{2} & \mathrm{a} & 1\end{array}\right|=\dfrac{1}{2} \cdot \dfrac{3 \mathrm{a}^{2}}{4}=\dfrac{3 \mathrm{a}^{2}}{8}$
$\dfrac{\mathrm{a}^{2}}{\dfrac{3 \mathrm{a}^{2}}{8}}=\dfrac{\lambda}{6} \Rightarrow \lambda=16$
Answer : b
19. A pair of perpendicular straight lines drawn through the origin form an isoceles triangle with line $2 x+3 y=6$, then area of the triangle so formed is
(a) $\dfrac{36}{13}$
(b) $\dfrac{12}{17}$
(c) $\dfrac{13}{5}$
(d) $\dfrac{17}{13}$
Show Answer
Solution: $\mathrm{OM}=\left|\dfrac{-6}{\sqrt{4+9}}\right|=\dfrac{6}{\sqrt{13}}, \mathrm{PQ}=2 \times \dfrac{6}{\sqrt{13}}$, area of $\triangle \mathrm{OPQ}=\dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{2 \times 6}{\sqrt{13}} \times \dfrac{6}{\sqrt{13}}=\dfrac{36}{13}$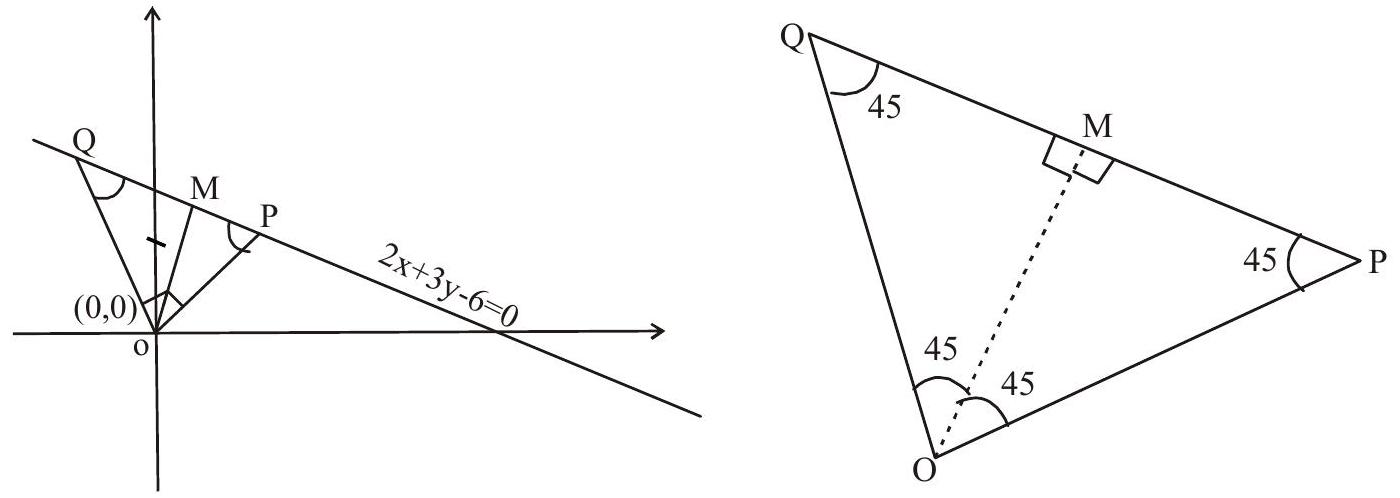
20. Match the column
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Two vertices of a triangle are (5,-1) and ( $-2,3)$ if orthocentre is origin then third vertex is | (p) | $(-4,-7)$ |
| (b) | A point on the line $x+y=4$ which lies at a unit distance from the line $4 x+3 y=10$, is | (q) | $(-7,-11)$ |
| (c) | Orthocentre of the triangle made by the lines $x+y-1=0, x-y+3=0,2 x+y=7$ is | (r) | $(1,-2)$ |
| (d) | If a,b,c are in A.P., then lines $a x+b y=c$ are concurrent at | (s) | $(-1,2)$ |
Show Answer
Solution:
A-p
B-q
C-s
D-s
Exercise
1. If $t _{1}$ and $t _{2}$ are roots of the equation $t^{2}+\lambda t+1=0$, where $\lambda$ is an arbitrary constant. Then the line joining the points $\left(a t _{1}{ }^{2}, 2 a t _{1}\right)$ & $\left(a t^{2}, 2 a t _{2}\right)$ always passes through a fixed point
(a) $(a, 0)$
(b) $(-a, 0)$
(c) $(0, a)$
(d) $(0,-\mathrm{a})$
Show Answer
Answer: b2. The equation $\mathrm{x}^{3}+\mathrm{y}^{3}=0$ represents
(a) three real straight lines
(b) three points
(c) combined equationof ast. line & a circle
(d) None of these.
Show Answer
Answer: d3. The three lines whose combined equation is $y^{3}-4 x^{2} y=0$ form a triangle which is
(a) isosceles
(b) equilateral
(c) right angled
(d) None of these
$\mathrm{A}(1,3)$ and $\mathrm{C}\left(-\dfrac{2}{5},-\dfrac{2}{5}\right)$ are the vertices of a triangle $\mathrm{ABC}$ and the equation of the angle bisector of $\angle \mathrm{ABC}$ is $\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y}=2$
Show Answer
Answer: dComprehension Type
4. Equation of side $\mathrm{BC}$ is
(a) $7 x+3 y=4$
(b) $7 x+3 y+4=0$
(c) $7 x-3 y+4=0$
(d) $7 x-3 y=4$
Show Answer
Answer: b5. Coordinates of vertex $B$ are
(a) $\left(\dfrac{3}{10}, \dfrac{17}{10}\right)$
(b) $\left(\dfrac{17}{10}, \dfrac{3}{10}\right)$
(c) $\left(-\dfrac{5}{2}, \dfrac{9}{2}\right)$
(d) $(1,1)$
Show Answer
Answer: c6. Equation of side $\mathrm{AB}$ is
(a) $3 x+7 y=24$
(b) $3 x+7 y+24=0$
(c) $13 x+7 y+8=0$
(d) $13 x-7 y+8=0$
Show Answer
Answer: a7. Assertion and reasoning Type
Lines $\mathrm{L} _{1} \mathrm{~L} _{2}$ given by $\mathrm{y}-\mathrm{x}=0$ and $2 \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y}=0$ intersect the line $\mathrm{L} _{3}$ given by $\mathrm{y}+2=0$ at $\mathrm{P}$ and $\mathrm{Q}$, respectively. The bisector of the acute angle between $\mathrm{L} _{1}$ and $\mathrm{L} _{2}$ intersects $\mathrm{L} _{3}$ at $\mathrm{R}$.
Statement 1 : The ratio PR: RQ equals $2 \sqrt{2}: \sqrt{5}$.
Statement 2 : In any triangle, bisector of an angle divides the triangle into two similar triangles.
a Statement 1 is true, Statement 2 is True; Statement 2 is a correct explanation for Statement1.
b Statement 1 is True, Statement 2 is True; Statement 2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement 1 .
c Statement 1 is True, Statement 2 is False.
d Statement 1 is False, Statement 2 is True.
Show Answer
Answer: c8. Matrix-match
This question contains statements given in two columns which have to be matched. Statements a, b, c, d in column I have to be matched with statements p,q, r, s in column II. If the correct match is a $\rightarrow \mathrm{p}, \mathrm{a} \rightarrow \mathrm{s}, \mathrm{b} \rightarrow \mathrm{q} \mathrm{b} \rightarrow \mathrm{r}, \mathrm{c} \rightarrow \mathrm{p}, \mathrm{c} \rightarrow \mathrm{q}$ and $\mathrm{d} \rightarrow \mathrm{s}$, then the correctly dubbled $4 \times 4$ matrix should be as follows :
Consider the lines given by
$\begin{aligned} & \mathrm{L} _{1}: \mathrm{x}+3 \mathrm{y}-5=0 \\ & \mathrm{~L} _{2}: 3 \mathrm{x}-\mathrm{ky}-1=0 \\ & \mathrm{~L} _{3}: 5 \mathrm{x}+2 \mathrm{y}-12=0 \end{aligned}$
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | $\mathrm{L} _{1}, \mathrm{~L} _{2}, \mathrm{~L} _{3}$ are concurrent, if | (p) | $\mathrm{k}=-9$ |
| (b) | One of $\mathrm{L} _{1}, \mathrm{~L} _{2}, \mathrm{~L} _{3}$ is parallel to at least one of the other two, if | (q) | $k=-6 / 5$ |
| (c) | $\mathrm{L} _{1}, \mathrm{~L} _{2}, \mathrm{~L} _{3}$ form a triangle, if | (r) | $\mathrm{k}=5 / 6$ |
| (d) | $\mathrm{L} _{1}, \mathrm{~L} _{2}, \mathrm{~L} _{3}$ do not form a triangle, if | (s) | $\mathrm{k}=5$ |





