Qualitative Analysis - Result Question 33
Passage
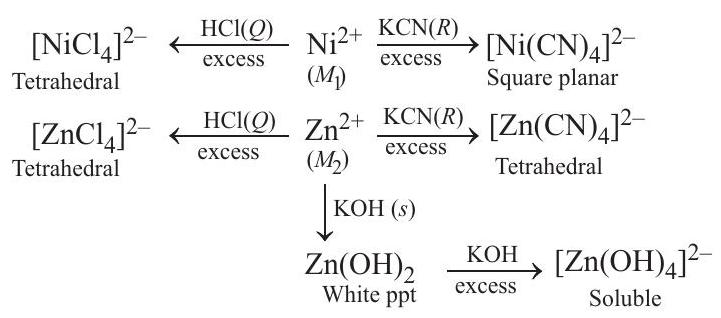
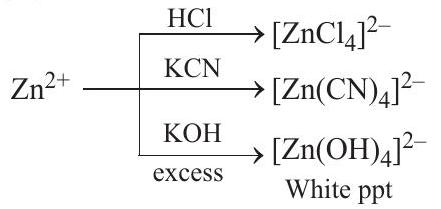
An aqueous solution of metal ion $M_1$ reacts separately with reagents $Q$ and $R$ in excess to give tetrahedral and square planar complexes, respectively. An aqueous solution of another metal ion $M_2$ always forms tetrahedral complexes with these reagents. Aqueous solution of $M_2$ on reaction with reagent $S$ gives white precipitate which dissolves in excess of $S$. The reactions are summarised in the scheme given below
34. $M _1, Q$ and $R$, respectively are
(a) $Zn^{2+}, KCN$ and $HCl$
(b) $Ni^{2+}, HCl$ and $KCN$
(c) $Cd^{2+}, KCN$ and $HCl$
(d) $Co^{2+}, HCl$ and $KCN$
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 34. (b)
Solution:
PLAN This problem can be solved by using concept of chemical reactions of transition metal ions (,) colour and structure of transition metal compounds.
Here, among given four option $Ni^{2+}$ and $Zn^{2+}$ has ability to form tetrahedral as well as square planar complex depending upon types of reagent used.
$Ni^{2+}$ on reaction with $KCN$ forms square planar complex $\left[Ni(CN) _4\right]^{2-}$ due to strong field strength of $CN$.
$Ni^{2+}+KCN \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Square planar }}{\left[Ni(CN) _4\right]^{2-}}$
While on reaction with $HCl, Ni^{2+}$ forms stable tetrahedral complex $\left[Ni(Cl) _4\right]^{2-}$.
$Zn^{2+}$, on the other hand, on reaction with $KCN$ as well as $HCl$ produces tetrahedral complex because of its $d^{10}$ electronic configuration.
Complete reaction sequence can be shown as