Current Electricity Ques 39
- In the given circuit, an ideal voltmeter connected across the $10$ $ \Omega$ resistance reads $2 $ $V$. The internal resistance $r$, of each cell is
(2019 Main, 10 April I)
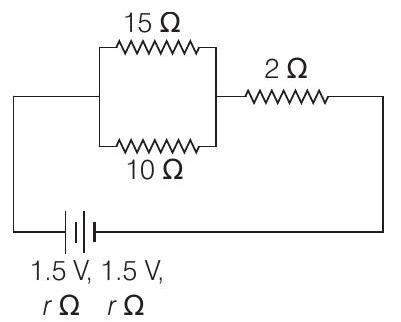
(a) $1.5 $ $\Omega$
(b) $0.5 $ $\Omega$
(c) $1 $ $\Omega$
(d) $0 $ $\Omega$
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 39.(b)
Solution:
- For the given circuit
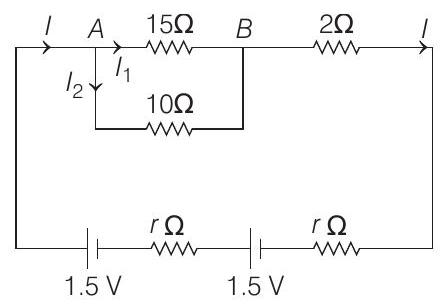
Given,
$ V _{A B}=2 V $
$\therefore$ Current in circuit,
$I=I _1+I _2 =\frac{2}{15}+\frac{2}{10} $
$ [\because V=I R \text { or } I=V / R] $
$=\frac{4+6}{30}=\frac{1}{3} A$ $\quad$ …….(i)
Also, voltage drop across $(r+r)$ resistors is
= voltage of the cell -voltage drop across $A B$
$ =3-2=1 V $
Using $V=I R$ over the entire circuit
$ \begin{array}{ll} \Rightarrow & 1=I(2+2 r)=\frac{1}{3}(2+2 r) \quad \text { [using Eq. (i)] } \\ \Rightarrow & 3=2+2 r \text { or } 2 r=1 \Omega \\ \text { or } & r=\frac{1}{2} \Omega=0.5 \Omega \end{array} $
Alternative Solution
Equivalent resistance between $A$ and $B$ is
$ \frac{1}{R _{A B}}=\frac{1}{10}+\frac{1}{15}=\frac{1}{6} \Rightarrow R _{A B}=6 \Omega $
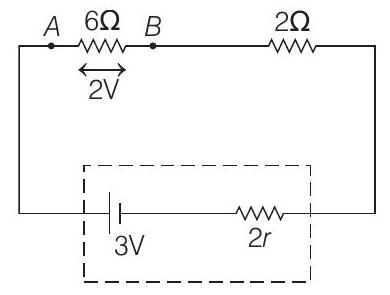
$\therefore$ Equivalent resistance of the entire circuit is, $R _{eq}$
$ =6 \Omega+2 \Omega+2 r=8+2 r $
Now, current passing through the circuit is given as,
$ I=\frac{E _{net}}{R+r _{eq}}=\frac{E _{net}}{R _{eq}} $
where, $R$ is external resistance, $r _{eq}$ is net internal resistance and $E _{\text {net }}$ is the emf of the cells.
$\text { Here, } \quad E _{\text {net }}=1.5+1.5=3 V $
$ r _{eq} =r+r=2 r $
$\Rightarrow \quad I=\frac{3}{8+2 r}$
Also, reading of the voltmeter, $V=2 V=I \cdot R _{A B}$
$2 =(\frac{3}{8+2 r}) \times 6 $
$\Rightarrow \quad 8+2 r =9 \quad \text { or } \quad r=\frac{1}{2}=0.5$ $ \Omega$





